Isolation of Stuzerimonas strain SH1 and characterization of its CAH removal capacity
A patented strain capable to degrade Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons (CAH)
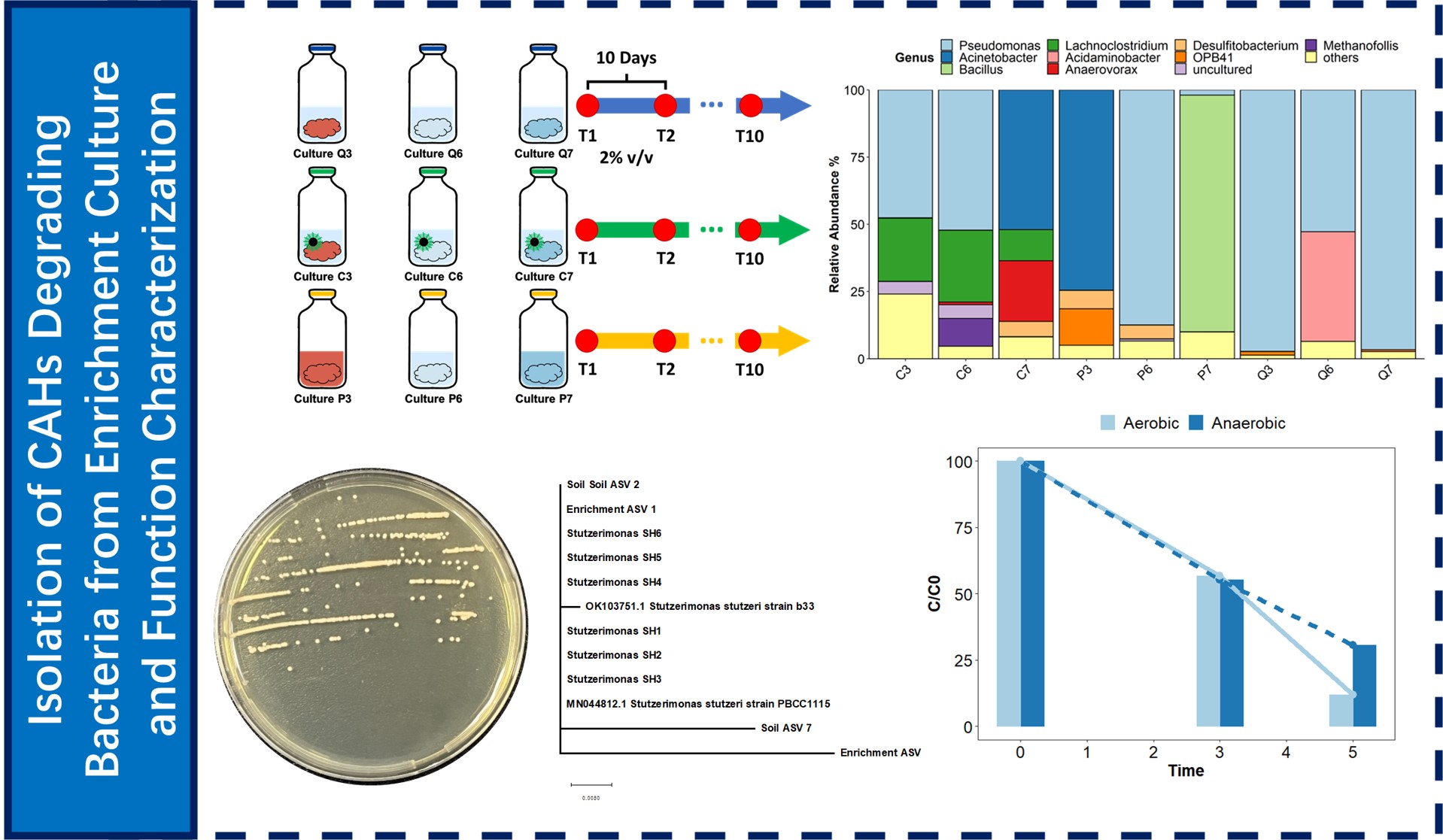
SJTU set up multiple batches of enrichment culture to construct an ideal model to study impact of nZVI on reductive dechlorinating microbial community. However, it was observed that an ASV affiliated to genus Stuzerimonas was enriched in several systems, the highest relative abundance reached as high as 97%. Multiple isolates were isolated from this enrichment culture and the 16S rRNA gene V3-V4 region sequence are 100% the same as the ASV in the sample from contaminated site. The isolate, strain SH1, is capable to remove over 90% and 60% of TCE within 5 days under aerobic and anaerobic conditions respectively with 0.5mM acetate amended. The anaerobic oxidative removal of highly chlorinated CAH (TCE) by this isolate has promising potential to be developed to novel bioremediation strategies. This strain has been patented (CN 2022115787175).
Partner Involved